Monetary Policy Implementation
Federal Funds Rate (FFR): interest rate for overnight lending between banks
- FFR set during FOMC meeting (every 6 weeks)
FFR ≠ Discount Rate
LR Curve: represents under Fed policy
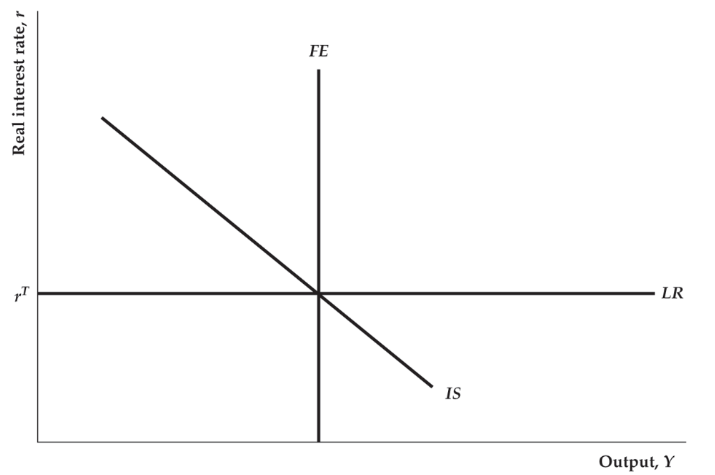
The Fed adjusts to hit
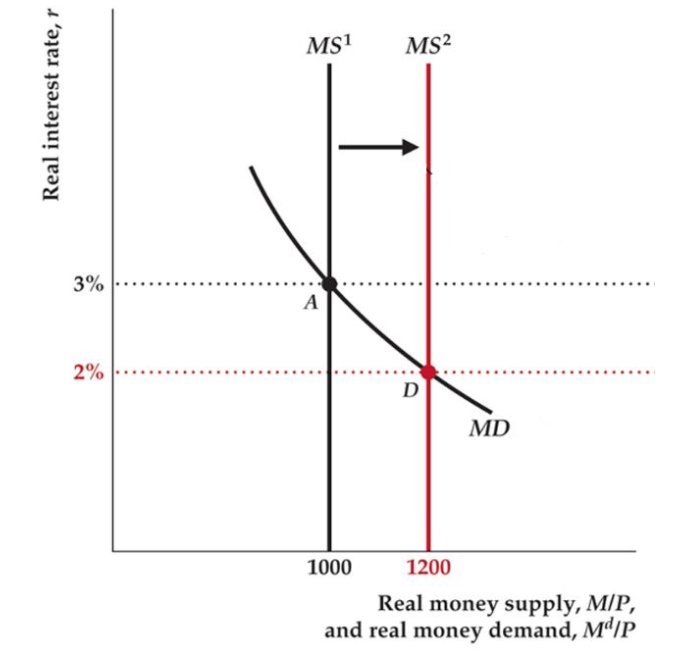
Shock Takeaways
Shocks to LM curve
- Fed stabilizes by maintaining same FFR target
Shocks to IS curve
- Fed needs to change target interest rate to stabilize output
- Substantial uncertainty about optimal FFR target
Why target FFR instead of M1?
Money demand changes frequently
- Would have to adjust M1 to maintain Money Market equilibrium
- FFR allows Fed to maintain same target
- works better to offset shocks to money demand
Why is it difficult to set the interest rate target?
- conflicting signals about state of economy
- lag in monetary policy (long and variable)
- Zero lower bound
Taylor Rule:
where:
: nominal FFR
: inflation rate over last 4 quarters
: equilibrium (usually assumed to be 2%)
: output gap = : % deviation of from
: is the weight; how much the Fed cares about inflation vs output (0.5 is neutral)
Fiscal Policy Implementation
- long lags due to political process
- lack in flexibility (gov committed years in advance)
- difficult to predict effects/size necessary stimulus compared to monetary policy
Automatic Stabilizers
Features of the structure of government budgets that act to dampen fluctuations in real GDP
e.g. Unemployment insurance, income tax, welfare programs
Government Budget Deficit
Deficit: when exceeds in any fiscal year
Debt: total amount of money owed by government to creditors at a particular time
Debt-GDP ratio:
low deficit relative to GDP debt-GDP ratio
high rate of GDP growth debt-GDP ratio
where:
: nominal value of government debt
: price level
: real GDP