Nominal wages tend to move with inflation so what are the costs of inflation?
5 Costs of Inflation
Menu Costs
Costs for firms in changing their prices.
- partly explained sticky prices in Keynesianism
Shoeleather Costs
Costs of holding less cash and putting it into interest bearing assets
- name comes from walking to and from the bank
Tax Distortions
You are taxed on the nominal interest rate which means that you pay more taxes when inflation rises even for the same real gain.
Unexpected Inflation
redistributes wealth, but not based on merit or need
- good for borrowers, bad for lenders/savers
Confusion/Misallocation of resources
inflation is yardstick to measure prices
- relative prices can vary if all the firms don’t raise prices at the same time
- this can distort the allocation of resources (resources allocated based on relative prices rather than actual market needs)
Optimal Rate of Inflation
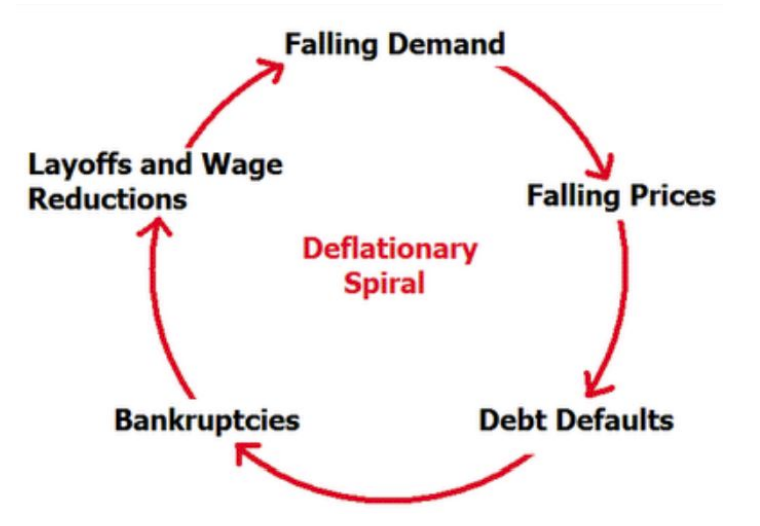
Not negative (deflation)
- has same 5 costs as inflation
- deflation spiral/negative feedback loop:
Optimal rate is positive
- Fed targets 2%
- 5 costs of inflation under low inflation (<10%) are small
- Some inflation prevents deflationary spiral
- positive inflation allows the FED to reach lower real interest rates (equal to )
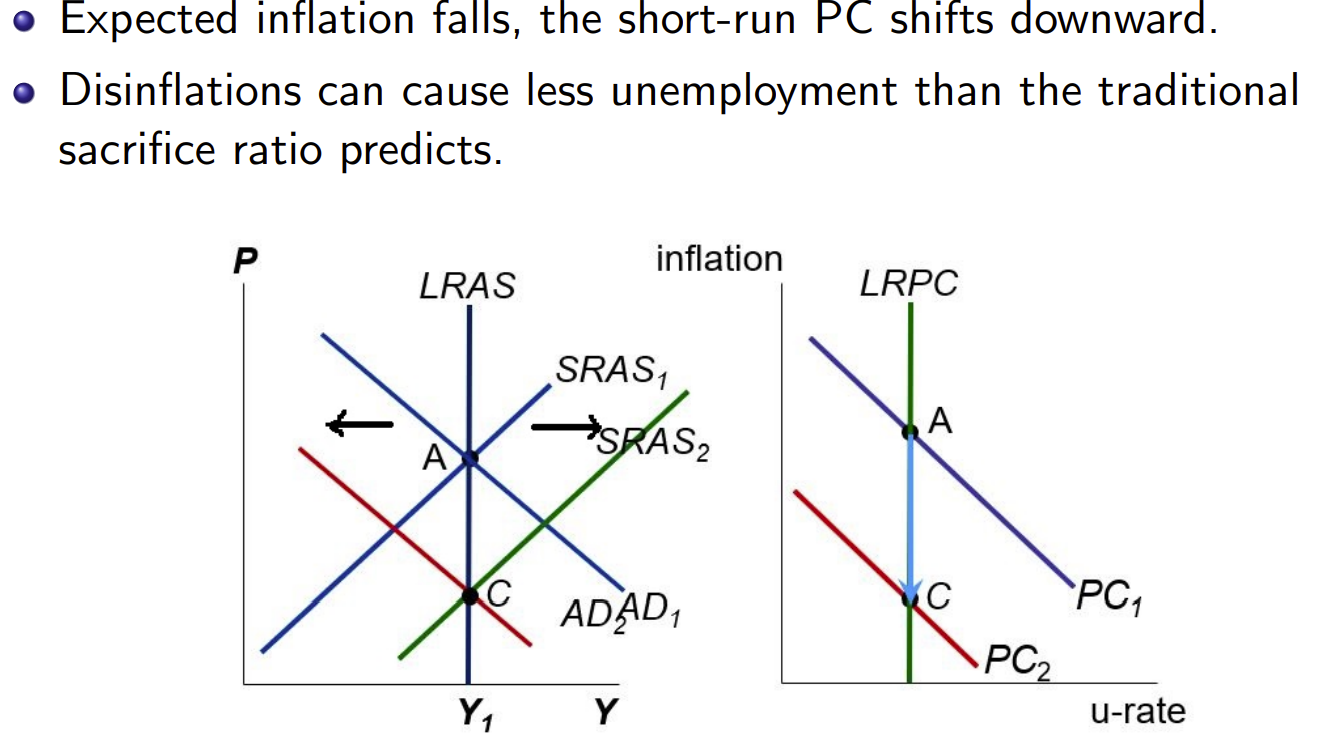
Disflationary Policy
Sacrifice Ratio: percentage points of SR output lost per 1 percentage point reduction in inflation
- estimated at 5 (sacrifice 5% output to reduce inflation 1%)
- can spread sacrifice over time → empirically sacrifice ratio much smaller
Rational Expectations
if the central bank can convince everyone it is committed to reducing inflation it will affect .