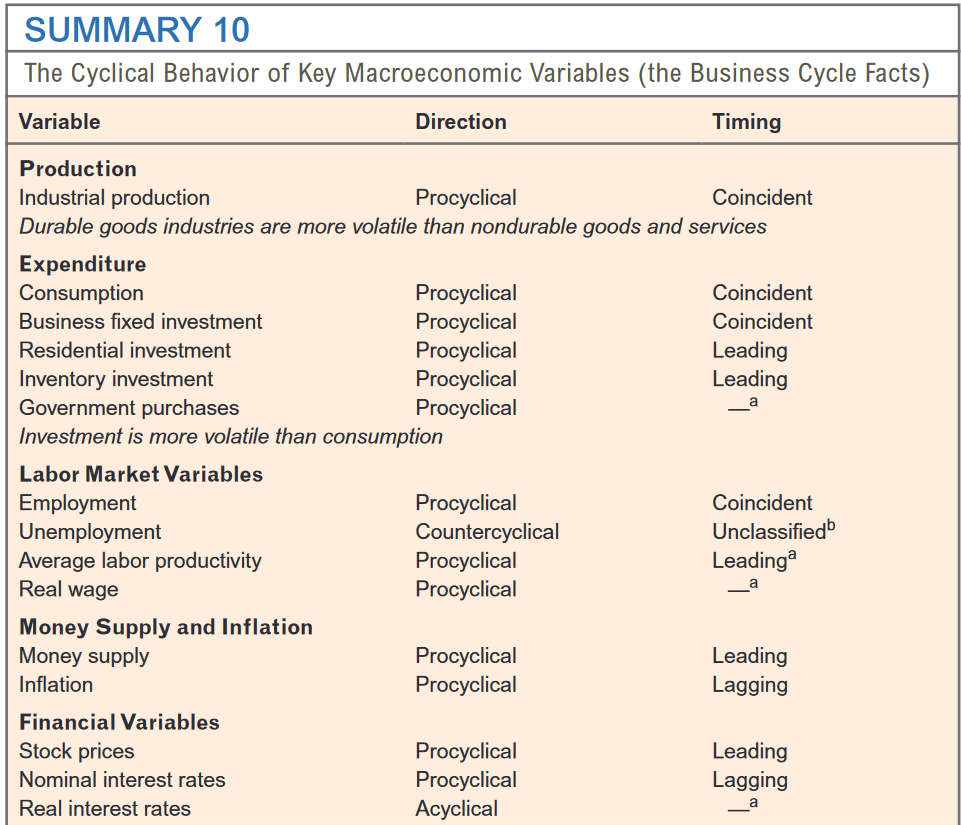
What are Business Cycles
Fluctuations of aggregate economic activity
not just single economic variable
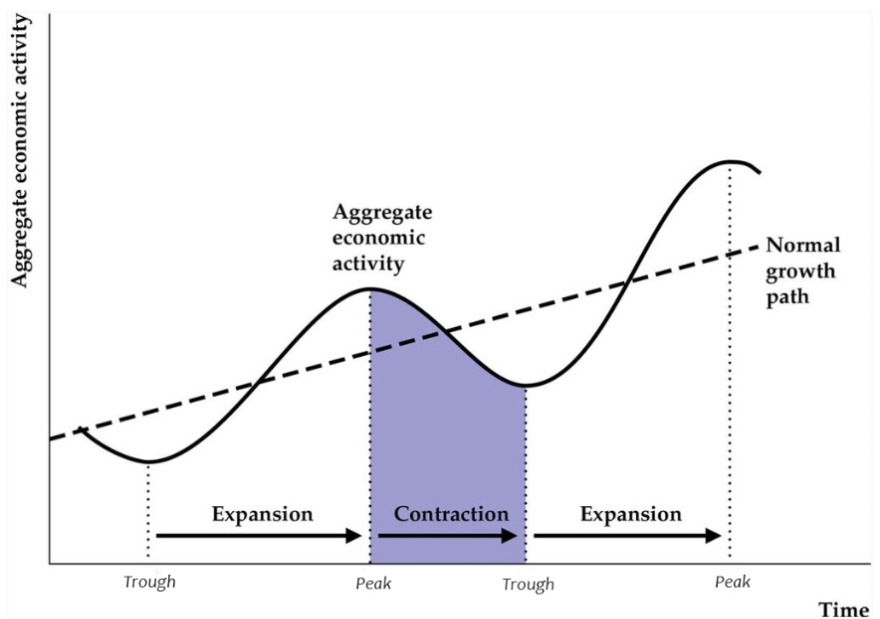
Expansion: Trough to Peak
Contraction: Peak to Trough
Business cycles are recurrent but not periodic
Predicting Business Cycles
Leading Variables
- Tend to fluctuate in advance of overall economy
- Examples:
- manufactures new orders of goods and materials
- average weekly initial claims for unemployment insurance
Problems with leading variables:
- Macroeconomic data often revised
- No single leading variable can perfectly predict business cycles
Coincident Variables
- Fluctuate simultaneously with overall economy
- Four major:
- Industrial production
- Manufacturing and trade sales
- nonfarm employment
- real personal income
Lagging Variables
Tend to fluctuate after the changes in overall economy
- CPI, Wages, Nominal interest rate
Comovement of Variables
Tendency of many economic variables to move together in a predictable way over the business cycle
Three kinds of comovement:
Procyclical
Variables move in same direction as aggregate economic activity
- real GDP, consumption, investment
Countercyclical
Variables move in opposite direction of aggregate economic activity
- Unemployment
Okun’s Law:
natural rate of unemployment
full-employment output
Thus a 1 percentage point increase in U 2% reduction in output relative to
Acyclical
Variables that do not have a clear pattern over business cycle
- Real interest rate